How do polarized lenses work?
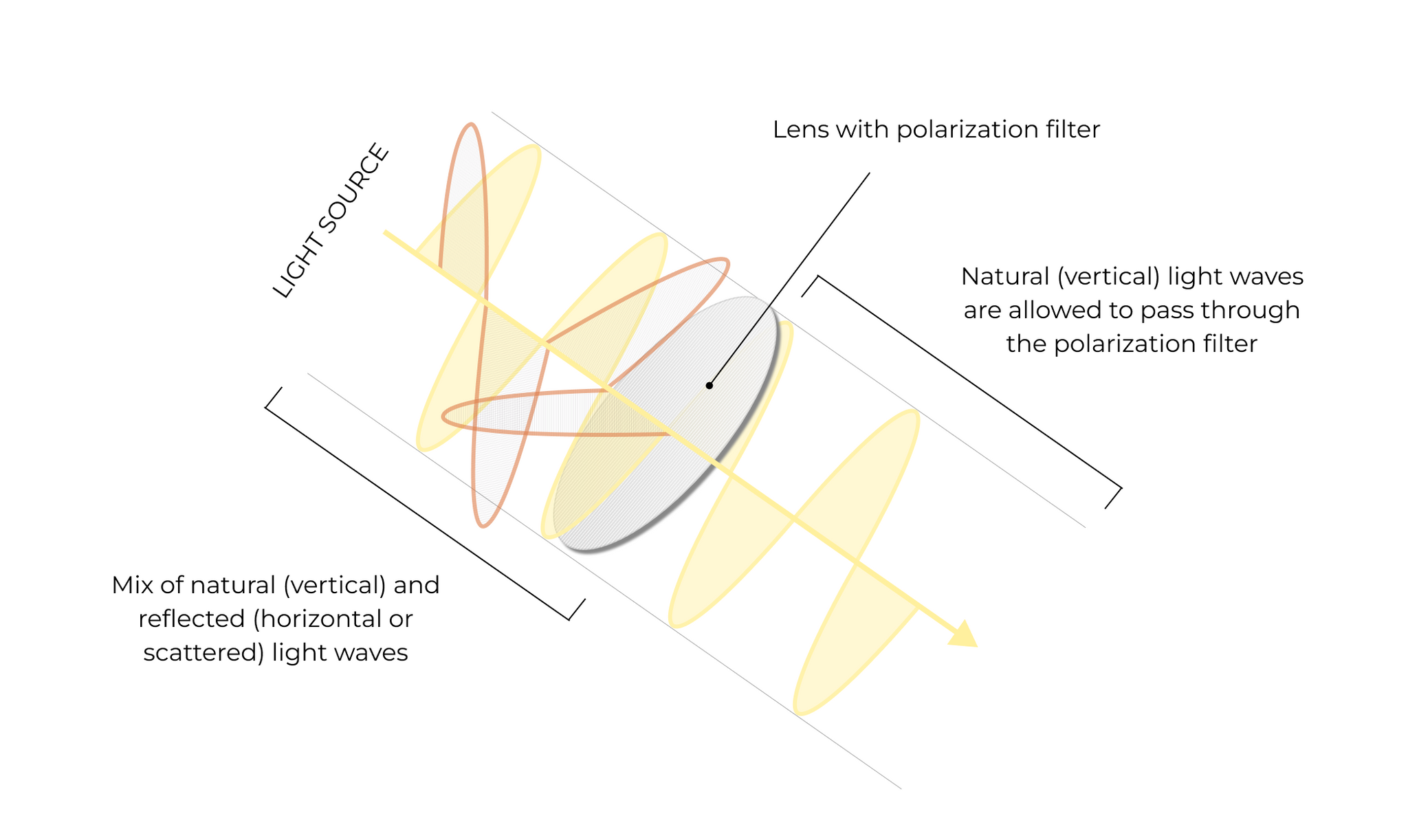
Our eyes are most used to ‘natural light’ (aka vertical light waves that are delivered directly from the source, such as our sun). However, when light is bounced off a reflective surface, such as water, windshields, or asphalt, it becomes ‘reflected light’.
Reflected light is made up of horizontal light waves, because the light waves have become scattered before they reach your eyes. (This is what our eyes perceive as glare, and what causes discomfort).
Polarized lenses help to filter this light before it reaches our eyes, letting raw, natural light (vertical light waves) pass through. By comparison, the reflected light (horizontal light waves) has a harder time passing through.
How are polarized lenses made?
The polarization filter is achieved by a chemical process whereby a long chain of hydrocarbons is placed onto Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA). The PVA is then heated, stretched, and dipped in iodine, resulting in a vertical grid effect (not visible to the naked eye). The final PVA is then positioned very close to the front curvature of the lens and helps block horizontal light waves whilst letting vertical ones pass through.
What are polarized lenses good for?

IMPROVED COMFORT
Reduced glare for comfort and protection
Glare impairs our vision when doing activities on or near highly reflective surfaces (water, asphalt, or windshields). In this scenario, your eyes don’t need to work as hard to interpret what they see beneath the surface. Glare causes fatigue, headaches, and eye strain as our eyes are working harder to interpret the mix of horizontal and vertical light waves. Over time, this results in safety issues as our ability to make decisions quickly is reduced. In these scenarios, polarized filters are excellent for improving vision, safety, and performance.
BETTER VISION
Better visibility on water
The qualities of polarized lenses lend them to sports where you need better visibility on the surface of the water, or indeed below it, such as:
- Fishing
- Sailing
- SUP
- Kayaking
- Canoeing
- Windsurfing
- Biking or driving on wet roads
LIGHT & SHADE
Enhanced contrast
In the process of reducing horizontal light waves and glare, polarized lenses also make your overall vision ever so slightly darker. However, they do carry the added benefit of enhancing contrast, particularly in shade.
VIBRANT COLORS
Natural colors are boosted
When looking at rich colour environments such as green forests or blue skies through non-polarized lenses, you may notice that they can appear dimmer than their true color, or even washed out. This is due to reflections bounced off of tiny particles in humid or polluted air.
By comparison, polarized lenses help stop these erratic reflections, helping you retain your true color perception. Subsequently, environments maintain their natural appearance, and deep colors.
What are polarized lenses bad for?

REDUCED PERCEPTION
Reduced perception on snow and ice
It is a common misnomer that polarized sunglasses and goggles are useful on snow and ice. In glacial and snow-laden environments - and particularly when moving at speed - polarized lenses actually make it harder to perceive and differentiate between different shades of white associated with snow and ice.
--A note for skiers--
When skiing and snowboarding, it is a matter of safety to be able to distinguish between patches of snow and ice, particularly when exploring in mixed light conditions. This is why VALLON Heron Glacier and Heron Mountain glasses are not made with polarized lenses.
RISK OF MOIRE
Distracting patterns on digital screens
Polarized lenses are brilliant for natural environments, but not useful when looking at screens. (You may have already experienced ‘moire patterns’ (an almost holographic-type effect) when looking at a digital screen through polarized lenses).
--A note for pilots--
Moire is not favorable for pilots who need to be able to look at LCD displays, and natural views. Even for seaplane pilots, it is critical to be able to see reflections off the surface of the water to judge altitude during landing and other operations. Polarized lenses are not the preferred lens type for pilots.
INCREASED COST
Manufacturing incurs additional expense
Because creating polarized lenses involves one more step during the manufacturing process, they incur an additional cost to produce. This cost is subsequently commonly passed onto customers, making your polarized sunglasses more expensive.
In summary, when people are looking to buy sports eyewear, there is a common misconception that polarized lenses are better, or a sign of higher-quality. It is useful to know how, and why polarized lenses work to determine if they will enhance your comfort and safety, so you can enjoy your chosen activity to the max.